Quick reference for W55MH32
The below pinout is for W55MH32L-EVB.
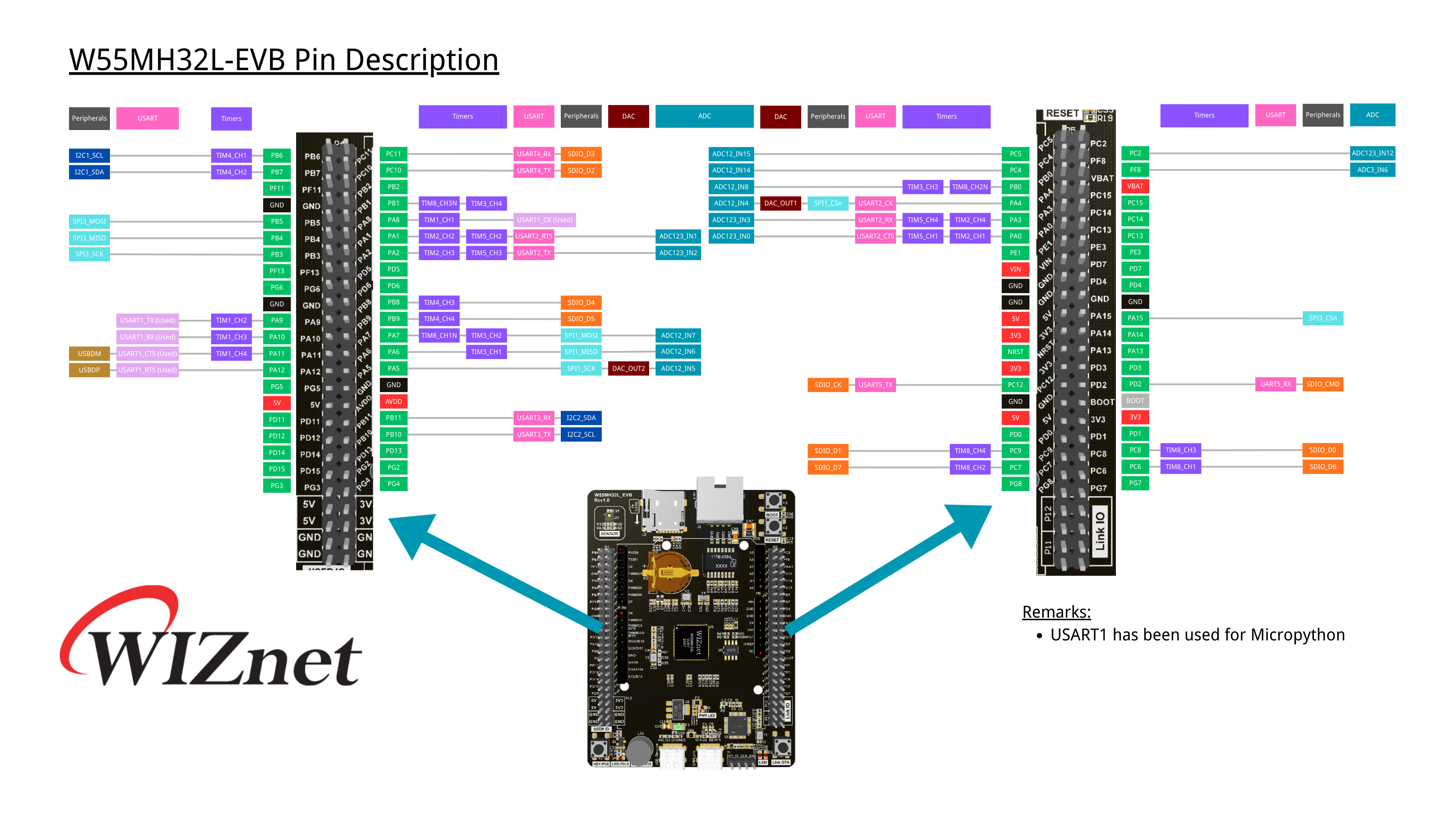
Below is a quick reference for the W55MH32L-EVB. If it is your first time working with this board please consider reading the following sections first:
General board control
The MicroPython REPL is on USART1 (PA9=TX, PA10=RX) at baudrate 115200. Tab-completion is useful to find out what methods an object has.
Networking
For testing the Ethernet feature of W55MH32L-EVB, it is required to do the followings.
Connect the board and PC with an Ethernet cable.
Set the IP address of the board and PC in the same IP segment.
Run the script and ping the board IP.
See network.WIZNET5K
import network
import time
from machine import SPI, Pin
NET_IP = "192.168.1.20"
NET_SN = "255.255.255.0"
NET_GW = "192.168.1.1"
NET_DNS = "8.8.8.8"
spi = SPI(2, baudrate=8_000_000, polarity=0, phase=0)
cs = Pin("PB12", Pin.OUT)
rst = Pin("PD9", Pin.OUT)
pwn = Pin("PE15", Pin.OUT, value =0)
nic = network.WIZNET5K(spi, cs, rst)
# Reset the WIZnet chip
nic.active(True)
# Please use your PC to Ping "192.168.1.20"
Delay and timing
Use the time module:
import time
time.sleep(1) # sleep for 1 second
time.sleep_ms(500) # sleep for 500 milliseconds
time.sleep_us(10) # sleep for 10 microseconds
start = time.ticks_ms() # get value of millisecond counter
delta = time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start) # compute time difference
Pins and GPIO
See machine.Pin.
from machine import Pin
p_out = Pin('PD14', Pin.OUT)
p_out.high()
p_out.low()
p_in = Pin('PG6', Pin.IN)
p_in.value() # get value, 0 or 1
Timers
See machine.Timer.
from machine import Timer
tim = Timer(1, freq=1000)
tim.counter() # get counter value
tim.freq(0.5) # 0.5 Hz
tim.callback(lambda t: print("callback!!!"))
RTC (real time clock)
See machine.RTC
from machine import RTC
rtc = RTC()
rtc.datetime((2017, 8, 23, 0, 1, 12, 48, 0)) # set a specific date and
# time, eg. 2017/8/23 1:12:48
# the day-of-week value is ignored
rtc.datetime() # get date and time
ADC (analog to digital conversion)
See machine.Pin and machine.ADC.
from machine import Pin, ADC
adc = ADC(Pin('PA4'))
adc.read_u16() # read value, 0-4095
DAC (digital to analog conversion)
See machine.Pin and machine.DAC.
from machine import Pin, DAC
dac = DAC(Pin('PA4'))
dac.write(120) # output between 0 and 255
UART (serial bus)
See machine.UART.
from machine import UART
uart = UART(2, 9600)
uart.write('hello')
uart.read(5) # read up to 5 bytes
SPI bus
See machine.SPI.
from machine import SPI
spi = SPI(1, baudrate=200000, polarity=1, phase=0)
spi.write('hello')
spi.read(5) # receive 5 bytes on the bus
I2C bus
See machine.I2C.
from machine import I2C
i2c = I2C(1 , freq=400000) # create hardware I2c object
i2c.scan() # returns list of peripheral addresses
i2c.writeto(0x38, 'hello') # write 5 bytes to peripheral with address 0x42
i2c.readfrom(0x38, 5) # read 5 bytes from peripheral
i2c.readfrom_mem(0x38, 0x10, 2) # read 2 bytes from peripheral 0x42, peripheral memory 0x10
i2c.writeto_mem(0x38, 0x10, 'xy') # write 2 bytes to peripheral 0x42, peripheral memory 0x10